SQL Health Assessment and Configuration of Alerts

Managing a SQL Server environment extends beyond routine maintenance. It demands a proactive strategy for optimal performance and reliability. A pivotal element of this approach is the thorough SQL Server Health Assessment, focusing on monitoring and alerts for specific errors and severity levels.
Understanding the Need for Alerts
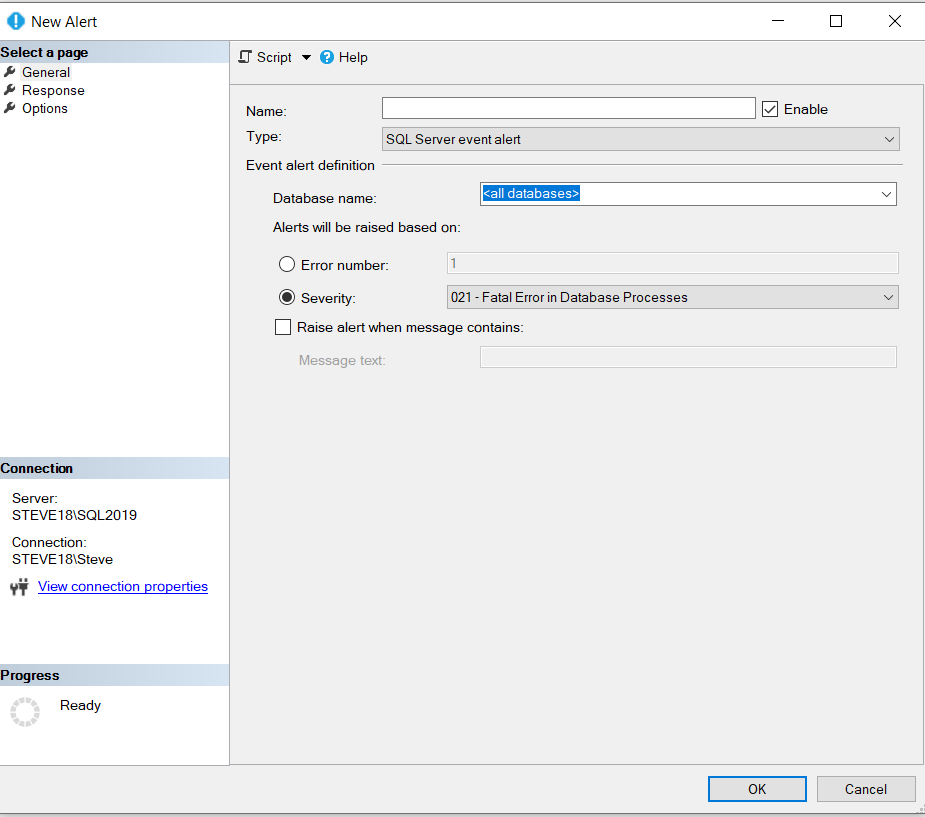
Alerts for severity levels 19 to 25 and errors 823, 824, and 825 are crucial in your SQL Server Health Assessment. These represent serious system issues. Severity levels 19 to 25 indicate critical problems needing immediate attention, while errors 823, 824, and 825 typically signal access difficulties in database files. These can lead to data loss or downtime if ignored, highlighting the importance of setting up alerts.
Step-by-Step Guide to Getting Set up
Set up is vital in the SQL Server Health Assessment. Here’s an effective approach:
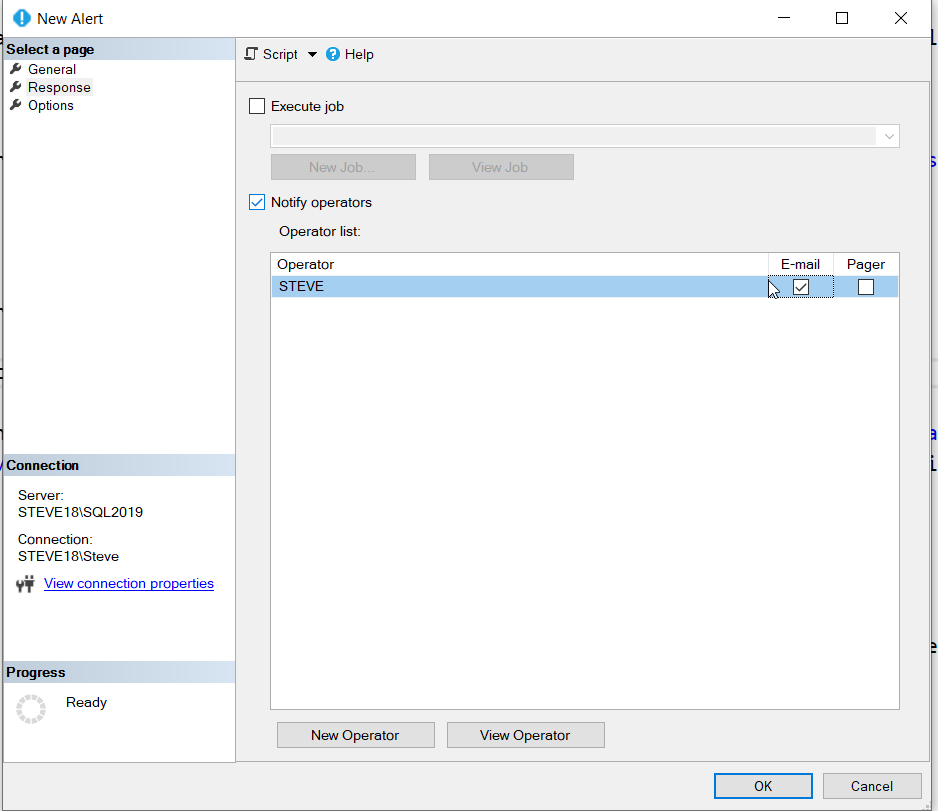
- Prepare for Notification: Ensure an operator is configured to receive notifications.
- Activate SQL Server Agent: The SQL Server Agent must be operational to send notifications.
- Configuring Alerts: In the SQL Server Agent, access the Alerts section to add and configure for each critical error.
- Save and Implement: After configuring, save the settings and repeat for each relevant error and severity level.
The Bigger Picture
Incorporating these tools in your SQL Server Health Assessment is crucial for preventing issues. Timely alerts enable immediate action, preventing minor issues from escalating. A comprehensive Health Assessment, alongside a well-configured alert system, is key to maintaining your SQL Server’s performance, security, and reliability.
If you need help setting up your alerts or with a SQL Server Health assessment at Stedman solutions, we can help. Just schedule a 30 minute free consult with Steve to determine how we can help.
Check out our other Database Health Monitor features like Schema Drift.
Leave a Reply