Replication Publishers and Subscribers
The Replication Publishers and Subscribers Report provides an overview of SQL Server replication configurations, including details about the publishers, subscribers, and their respective statuses. This report is particularly useful for monitoring and troubleshooting replication issues across your SQL Server environment.
Report Information
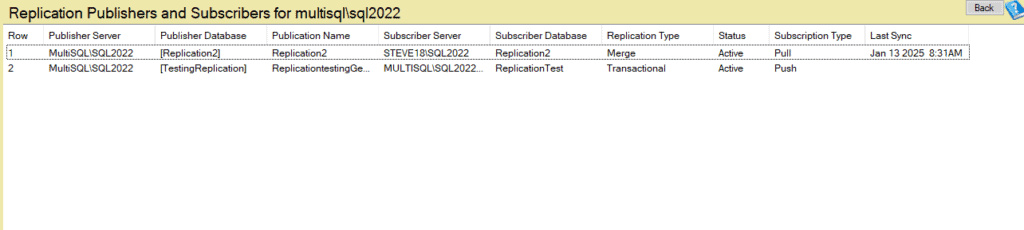
- Publisher Server
The name of the SQL Server instance hosting the publisher database. This is the server initiating the replication process by making data available to subscribers. - Publisher Database
The name of the database on the publisher server that is configured for replication. This is the source database for the replicated data. - Publication Name
The name of the publication, which defines the data and objects being replicated. Publications group articles (tables, views, stored procedures, etc.) to manage and control what is replicated. - Subscriber Server
The name of the SQL Server instance receiving replicated data. This server processes updates or changes from the publisher and stores them in the subscriber database. - Subscriber Database
The database on the subscriber server where replicated data is stored. This database acts as the destination for the replicated data. - Replication Type
Indicates the type of replication used for the publication. Possible values include:- Merge: Changes are tracked on both the publisher and subscriber, and updates are synchronized bidirectionally.
- Transactional: Changes are replicated continuously or periodically from the publisher to the subscriber in near real-time.
- Snapshot: A complete snapshot of the data is sent from the publisher to the subscriber at specific intervals. This type is ideal for scenarios where data changes infrequently or periodic updates suffice.
- Status
The current status of the replication process. Examples include:- Active
- Subscribed
- Inactive
- Last Sync
The timestamp of the last successful synchronization between the publisher and the subscriber. This information is crucial for understanding the recency of data replication and identifying potential delays.
Use Cases
This report is ideal for:
- Monitoring real-time health of SQL Server replication setups.
- Identifying replication issues such as stale subscribers, inactive publications, or errors.
- Validating configurations when troubleshooting replication performance.
- Ensuring compliance with business continuity and disaster recovery requirements by keeping replication in sync.
How Stedman Solutions Can Help
If you encounter challenges managing or troubleshooting SQL Server replication, Stedman Solutions is here to help. Our team can assist you and your business with:
- Designing and implementing robust replication strategies.
- Optimizing performance for transactional and merge replication.
- Resolving errors and ensuring synchronization reliability.
Learn more about our SQL Server Consulting and Managed Services, or contact us directly at Contact Us.